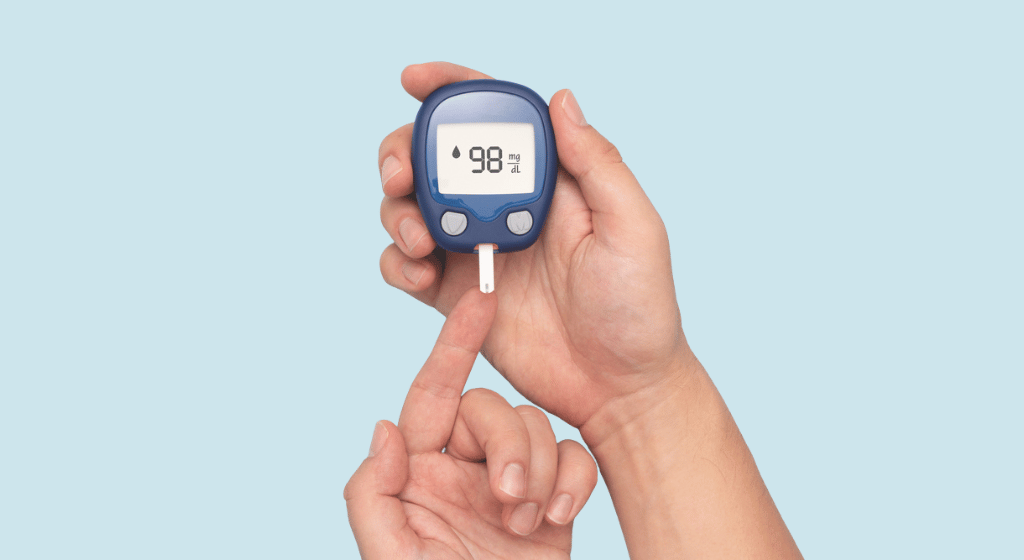
Recognizing 14 Early Indicators of Elevated Blood Sugar Levels and Dietary Approaches for Reversal
If there is one particularly debilitating disease, it is diabetes. Diabetes is characterized by high levels of sugar in the bloodstream, and it can affect individuals for different reasons, and the reasons vary from person to person. Before delving into the 14 basic symptoms of diabetes, it is important to understand its various causes to treat them proactively.
The causes of diabetes can be classified into three types: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes during pregnancy. This discussion focuses on type 2 diabetes, which is the most common form. The primary factors that contribute to type 2 diabetes include genetic predisposition, sedentary lifestyles leading to insufficient physical activity, and the interrelated issues of obesity and poor dietary habits. In addition, aging increases the risk of diabetes. Recognizing these risk factors is vital to spot symptoms promptly.
Here are the 14 main symptoms of diabetes that are worth paying attention to, especially for people at risk:
- Frequent urination, especially at night, may indicate diabetes.
- Blurred vision, not related to previous vision problems, can be a sign of diabetes.
- Persistent dry mouth, even after drinking water, may indicate diabetes.
- Increased thirst is often accompanied by dry mouth, which indicates diabetes.
- Impotence or fertility problems may be related to diabetes.
- Slow healing of cuts and wounds is a common consequence of diabetes.
- Poor concentration is one of the symptoms associated with diabetes.
- Repeated infections, along with delayed wound healing, may indicate diabetes.
- Digestive problems such as nausea and vomiting can be linked to diabetes.
- Increased appetite, along with normal hunger, may be a symptom of diabetes.
- Nerve problems that cause pain in the legs, arms, or feet can be an indication of diabetes.
- Skin problems such as dryness, itching, and susceptibility to infections may result from diabetes.
- Weight gain, especially around the waist, is a sign and result of diabetes.
While these symptoms cannot be completely eliminated, their effect can be managed, especially by following a balanced diet. Consuming foods with a low GI is crucial, because foods with a high GI can raise blood sugar levels. Recommended low glycemic foods include broccoli, nuts, chickpeas, eggs, cashews, yogurt, cherries, medium apples, Turkish sausage, medium onions, green grapes, pasta, tomato juice, carrots, peas, pineapple juice, and bananas. , grapefruit, and orange. Moderation is key, with a suggested limit of one cup per day.
It is also important to avoid high-glycemic foods such as popcorn, white rice, white bread, potatoes, cornflakes, glucose, processed meals, and sweet meats. Balancing a healthy diet with regular exercise is key in controlling diabetes. Neglecting these aspects can have serious consequences, underscoring the need for proactive diabetes management to prevent it from getting out of control.